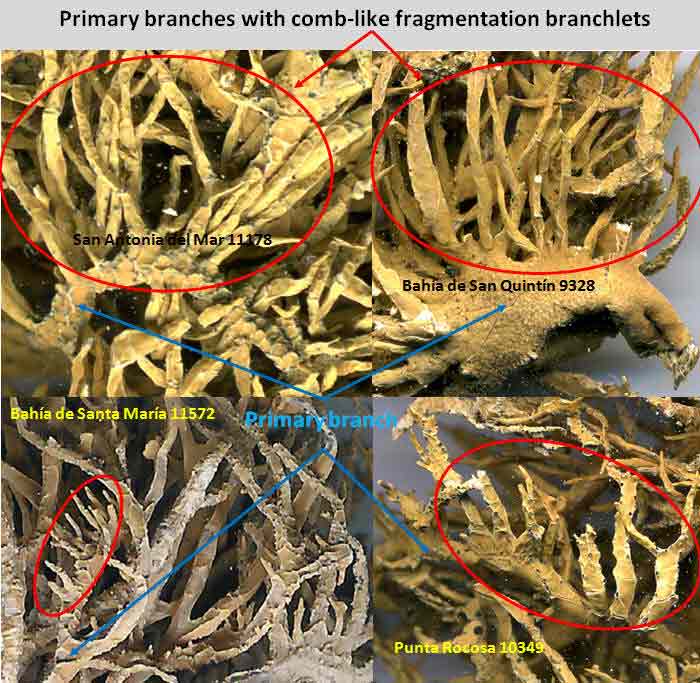
Niebla josecuervoi
is a fruticose lichen endemic to the Baja California peninsula, occurring along the
Pacific Coast from Morro Santo Domingo north to Ejido Erendira, usually on rocks, occasionally terricolous.
Niebla
josecuervoi is recognized by having salazinic acid without triterpenes, and
by a thallus of primary sublinear branches bearing secondary (lateral) comb-like
branchlets along one side; the primary branches often decumbent with the lateral
branchlets erect, and frequently short-bifurcate near apex.
Apothecia usually develop on the spinuliferous (fragmentation) branchlets. Most thalli bear
apothecia (>90%, Spjut 1996) in contrast to the terricolous
N.
effusa (salazinic acid) with less frequent apothecia (~66%, Spjut 1996) and
with the fragmentation branchlets confined more to an apical dilated branch.
Another related salazinic-acid species, N. arenaria,
in which apothecia are rarely
present, has a thallus more intricately divided terminating in short bifurcate spine-like (acicular) branchlets.
Occasionally, fragmentation branchlets are not evident in N. josecuervoi,
the species then recognized by the
± uniformly linear shape of the branches
throughout with prominent reticulate cortical ridging.
Unlike
Niebla arenaria
that occasionally forms a
single dominant
Niebla community, N. josecuervoi
is usually a member of a multi-species Niebla community. In its northern
range, such as in the coastal chaparral region between San Quintín and San
Vicente, it occurs on rocks with N. fimbriata
(sekikaic acid). Around Bahía
de San Quintín it is commonly associated with N. homalea
(divaricatic acid), N. eburnea (divaricatic
acid) and N. juncosa var. spinulifera (divaricatic acid).
In the CDT southwest of El Rosario, terricolous forms
grow on lava mesas in association with N. effusa
(salazinic acid), N. arenaria (salazinic
acid), and N. juncosa var. spinulifera. In the NVD, it is saxicolous, primarily with
N. turgida (divaricatic
acid) on Mesa Santa Catarina and along beaches with N. flabellata (salazinic acid).
Further south, it is associated with numerous species of Niebla,
especially in a highly diverse Niebla community on Mesa Camacho.
South of Punta Rocosa,
N. josecuervoi is replaced by N. marinii (salazinic acid) as seen at
Morro Santo Domingo where N. marinii is
notably dominant in a Niebla community that included
N. lobulata
and N. juncosa var. juncosa within a higher plant community of Joshua tree woodland of
Yucca
valida; however, intermediate forms are evident by specimens having a shiny
smooth cortex with the typical fragmentation branchlets, in contrast to
the rough cortex of N. josecuervoi.
They are further separated by the flexuous curved branches seen in N. marinii
in contrast to the rigidly stiff and straight branches that characterizes N.
josecuervoi. Both species were named after field assistants; José Cuervo is
also a well-known name for a brand of Tequila (Wikipedia).
Niebla josecuervoi
is also morphologically similar to N. fimbriata (sekikaic acid),
N. palmeri,
N.
turgida (divaricatic acid), N. juncosa (divaricatic acid, and
N.
pulchribarbara (protocetraric acid). They are easily identified by their lichen substances.
A proposed new species with salazinic acid species, (N. angulata Spjut ined.),
differs by the
basal branches dividing equally into secondary branches segments as seen in N.
marinii by examples of images presented. Another salazinic-acid
species, N. flabellata, differs by
the thallus divided into small tufts of flattened lacerated
branches.
An ITS phylogenetic tree (draft, unpublished) combining data from Spjut
et al. (2020) and (Jorna et al. 2021, Leavitt comm.) shows Niebla josecuervoi in two
or three clades including specimens from the type locality (nr San Quintín, Volcan Sudoeste) where
one clade appears sister to the
N. spatulata complex on the
Vizcaíno Peninsula. Spjut et al. (2020) in a BPP analysis of five
specimens of N. josecuervoi (sensu Spjut 1996) determined that
they represent four species, overlapping with undetermined character
traits for other depsidone species. Jorna et al. (2021), employing
numerous loci obtained from high-throughput sequencing could recognize nine depsidone species from a BPP analysis as also by Spjut et al. (2020)
based on six loci, while both studies also found that as few as three
species may be represented employing other analytical methods.
Although the depsidone clade would appear of more recent
derivation as related to its endemism to the NVD and CDT, N.
josecuervoi still includes cryptic species and shows disjunct
phylogeographic relationships as also seen in the more widely distributed depside clades.
The type specimen for N. josecuervoi was reported in the private
herbarium of Rundel (Rundel et al. 1972), while a later report by the
University of California at Los Angeles (LA) mentioned the Rundel lichen
collections at LA were transferred to RAMK in 2007.
Rakotondraibe, Spjut
& Addo (2024) reported on the isolation of the maleidride deoxyscytalidin
from N. josecuervoi, Spjut & Marin 13843.
Maleidrides, which are known primarily from filamentous fungi and for
their unusual biosynthetic pathway, belong to a family of polyketides
that account for the majority of novel bioactive compounds discovered from endolichenic fungi (Williams et al. 2023; Zhang et al. 2024).
This includes anticancer activity reported for a rubratoxin isolated from Penicillium sp. (Williams et al. 2023;
Zhang et al. 2024). Tan et al. (2019, 2020) and Anaya-Eugenio et
al. 2020) reported on the discovery of other active compounds from the
endlolichenic
Penicillium aurantiacobrunneum
isolated from
Niebla homalea.
References
Ermias Mekuria Addo, Dmitriy Uchenik,
Manead Khin, Richard W. Spjut, Joanna E. Burdette, A.
Douglas Kinghorn, Liva Harinantenaina Rakotondraibe. Unpublished,
abstract, Aug 2022. Dereplication and
Isolation of Secondary Metabolites of the Two Selected Pacific Coastal
Lichens. Species determination of Niebla josecuervoi,
Spjut & Marin 11386. Division of Medicinal Chemistry and Pharmacognosy; College of
Pharmacy, The Ohio State University; College of Pharmacy, University of
Illinois at Chicago; and World Botanical Associates.
Anaya-Eugenio G.D., Tan C.Y., Rakotondraibe L.H., Carcache de Blanco E.J.
(2020) Tumor suppressor p53 independent apoptosis in HT-29 cells by
auransterol from Penicillium aurantiacobrunneum. Biomed.
Pharmacother.
127:110124. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110124.
Rakotondraibe H L R, Spjut R W, Addo E M. 2024. Chemical
Constituents Isolated from the Lichen Biome of Selected Species Native
to North America. Prog Chem Org Nat Prod. 2024;124:185-233. doi:
10.1007/978-3-031-59567-7_3. PMID: 39101985 (see page 205 for structure
of deoxyscytalidin).
Tan C.Y., Wang F., Anaya-Eugenio G.D., Gallucci J.C., Goughenour K.D.,
Rappleye C.A., Spjut R.W., Carcache de Blanco E.J., Kinghorn A.D.,
Rakotondraibe L.H. (2019) α-Pyrone and sterol
constituents of
Penicillium aurantiacobrunneum, a fungal associate of the lichen
Niebla homalea. J. Nat. Prod. 82:2529-2536.
Tan CY. 2020. Identification
and Dereplication of Bioactive Secondary
metabolites of Penicillium aurantiacobrunneum,
a Fungal Associate of
the
Lichen Niebla homalea. Ph.D. Dissertation, The Ohio State
University.
Williams K, Szwalbe AJ, de Mattos-Shipley KMJ, Bailey AM,
Cox RJ, Willis CL. Maleidride biosynthesis - construction of dimeric
anhydrides - more than just heads or tails. Nat Prod Rep. 2023 Jan
25;40(1):128-157.
doi:
10.1039/d2np00041e. PMID: 36129067; PMCID: PMC9890510.
Zhang W, Ran Q, Li H, Lou H. Endolichenic Fungi: A
Promising Medicinal Microbial Resource to Discover Bioactive Natural
Molecules—An Update. Journal of Fungi. 2024;
10(2):99.
https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10020099
Additional References: See
Niebla.